Financial Conduct Authority says corporate boards can use sex not gender
The Financial Conduct Authority has issued new rules requiring listed companies to report on the proportion of women on corporate boards, scrapping its earlier proposal to require this to be based on gender self-identification.
439 people and organisations (over 80% of respondents) raised the issue of gender vs sex in their response to the consultation. Of those, 438 opposed the self-ID proposal and one supported it.
The FCA u-turn also follows a decision in the Scottish Inner House where For Women Scotland succeeded in their appeal challenging similar legislation which redefined “women” as a gender identity in relation to public boards in Scotland.
The new regulations allow companies to continue to report the composition of the board based on sex, or to chose to report based on gender identity if they wish. This is an awkward, face-saving compromise for the Stonewall Champion, but it steps back from imposing gender identity on thousands of major businesses.
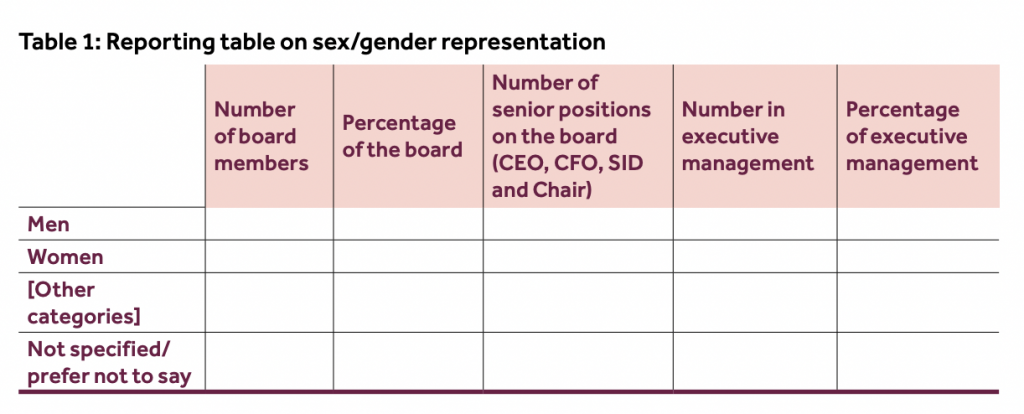
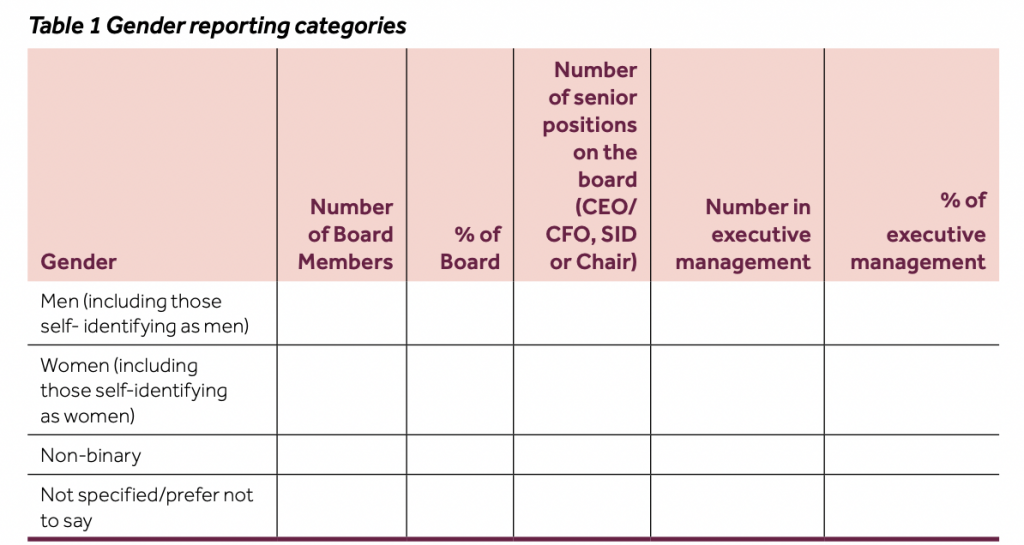
The FCA’s policy requires listed companies to publish data on the number of men and women on their boards, and to say whether this is based on sex or gender identity. They are required to report against targets of:
- at least 40% of board members being women
- at least one of the senior board positions being held by a woman.
Sex Matters, Legal Feminist, For Women Scotland and Sex not Gender all responded to the consultation highlighting that reporting on gender identity creates problems for data protection and privacy, and conflicts with existing requirements under the Companies Act to report data on sex.
In response to the issue of data protection, the FCA said it recognises that:
“collection and publication of personal data on sex has been workable in the context of UK data protection law to date and our final rules enable issuers to use the same data for the purposes of reporting under our rules.”
The new regulations leave it open for companies to chose to report on gender identity:
“We have removed the guidance on self-identification which accompanied the targets and data disclosure table and … given companies more flexibility to determine how best to collect data from employees.”
They must be consistent in applying this to everyone on the board, and all companies must explain whether they are reporting on sex or gender identity data.
Although the category “non-binary” was scrapped, companies that choose to report based on gender identity can also add “other categories” if they choose.
Maya Forstater, Executive Director of Sex Matters, said:
“The FCA was wise to allow companies to report straightforwardly on the proportion of male and female members of their boards, in line with the Equality Act and the Companies Act, and not to start requiring them to ask board members to declare that they have one of many fluid “gender identities”. It is not for the financial regulator to redefine what ‘man’ and ‘woman’ mean.”
City lawyer Cathy Pitt, who is a member of the Sex Matters advisory group, said:
“Collecting and reporting data on sex remains important, because how else can we measure improvement on closing the gap between men and women? Large listed firms still need to tackle sex-based discrimination on everything from pay and promotion to harassment and corporate culture.”
Companies that remain part of the Stonewall Champions Scheme are likely to come under pressure to collect data on the gender identity of board members, and not their sex, but they should consider the risk of belief discrimination from requiring all board members to declare their position on gender-identity questions.
They should also consider the opinion of the Inner Court in Scotland which declared that it was outside the Scottish Government’s competence to redefine the word “woman” as a protected characteristic in via The Gender Representation on Public Boards (Scotland) Act 2018. Lady Dorrian, said:
“By incorporating those transsexuals living as women into the definition of woman, the 2018 Act conflates and confuses two separate and distinct protected characteristics.”
As the FCA said “issuers should also be reminded that they remain subject to equalities legislation, including the Equality Act 2010 and its provisions on discrimination.” Accepting the FCA’s invitation to discard sex and instead adopt novel categories which conflate and confuse two separate and distinct protected characteristics creates risks of discrimination which general counsels should be wary of.
